(#111) 10 Key Insights from DeepSeek; The bull case for META
Amazon’s challenges in Argentina
Today’s Insights:
10 Key Insights from DeepSeek
Amazon’s challenges in Argentina
The bull case for META
Microsoft’s earnings and AI strategy
Working on a start-up
Where you live shapes who you become
On to the update:
10 Key Insights from DeepSeek
1/ DeepSeek has matched USA AI capabilities, despite sanctions showing that sanctions work (!)
DeepSeek’s latest models, particularly V3 and R1, demonstrate that China has caught up with OpenAI and Anthropic in AI reasoning and efficiency. When hardware and software restrictions exist, you look for efficiency and rethink everything, which DeepSeek did.
2/ DeepSeek’s AI is shockingly cheap to train
DeepSeek trained V3 for just $5.6 million, leveraging optimized architecture and resource-efficient training techniques. This raises existential questions for US AI firms that have been pouring billions into AI infrastructure.
3/ China found a way around US chip sanctions
The H800 GPU (from NVIDIA for the Chinese market), which lacks the memory bandwidth of the banned H100, was assumed to be insufficient for cutting-edge AI. DeepSeek’s breakthroughs show that Chinese AI labs can compete without high-end US chips by optimizing models for limited hardware.
4/ Distillation is undermining AI moats
DeepSeek likely used model distillation*, extracting insights from OpenAI and Anthropic’s APIs to train its models. This exposes a fundamental weakness in the AI industry, that is, leading-edge firms are bearing all the costs while others freeride on their advances.
5/ Big tech’s AI business model is crumbling
The ability to train high-performance AI at a fraction of previous costs means AI models are becoming a commodity. This directly challenges the business models of OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft, which rely on AI exclusivity and high cloud computing spending.
6/ DeepSeek’s open-source strategy could redefine AI
Unlike OpenAI’s closed approach, DeepSeek is open-sourcing its AI models to attract talent and accelerate global adoption. This mirrors China’s broader tech strategy: using cost efficiency and open access to dominate emerging industries.
7/ Nvidia’s AI dominance is under threat
DeepSeek’s efficiency optimizations mean AI can be trained and run on less powerful hardware, reducing reliance on Nvidia’s high-margin GPUs. If alternative computing solutions emerge, Nvidia’s growth story could unravel.
8/ Microsoft is reassessing its AI investments
The rapid commoditization of AI is why Microsoft is stepping back from exclusive AI investments like OpenAI’s Stargate project. Instead, it’s shifting toward a more fungible, cost-efficient AI infrastructure strategy.
9/ Google faces the biggest threat
If AI becomes cheap and widely available, Google’s search business is most at risk. AI-powered assistants could replace search queries, and Google’s TPU advantage could diminish if AI training costs continue to plummet.
10/ AI acceleration is inevitable
DeepSeek’s advancements confirm the “AI takeoff” scenario, where AI models self-train, optimize, and improve exponentially. The debate is no longer if AI will reshape industries, but how fast and who will control it. Dario Amodei, FT, WSJ, Bloomberg
* distillation - is a technique where a smaller or more efficient AI model learns from a larger, more powerful model by mimicking its outputs. Essentially, it’s a way to compress knowledge from a high-performing AI into a leaner, more optimized version without needing the full computational cost of training from scratch. Why it matters:
Amazon’s challenges in Argentina
Interesting insights coming out of Argentina:
1/ Amazon’s $5 shipping promise is not enough to overcome Argentina’s complex import system
While Amazon introduced a flat $5 shipping fee to Argentina, high customs duties and bureaucratic delays often double or triple the final cost, making international purchases less attractive. Many consumers find the overall expense still too high, especially when factoring in long delivery times.
2/ Mercado Libre’s dominance and local smuggling networks are Amazon’s biggest obstacles
MercadoLibre, Argentina’s homegrown e-commerce giant, has an extensive logistics network that Amazon struggles to match. Meanwhile, smugglers known as bagayeros continue to import goods informally, offering faster and often cheaper alternatives, especially for low-ticket items.
3/ Argentina’s economic policies are shifting, but consumer habits take time to change
Recent policy changes have reduced some import taxes, but most Argentines remain unfamiliar with or skeptical of Amazon’s system. With MercadoLibre deeply embedded in everyday shopping habits, Amazon’s impact may remain limited unless more consumers become comfortable with international purchases. LINK
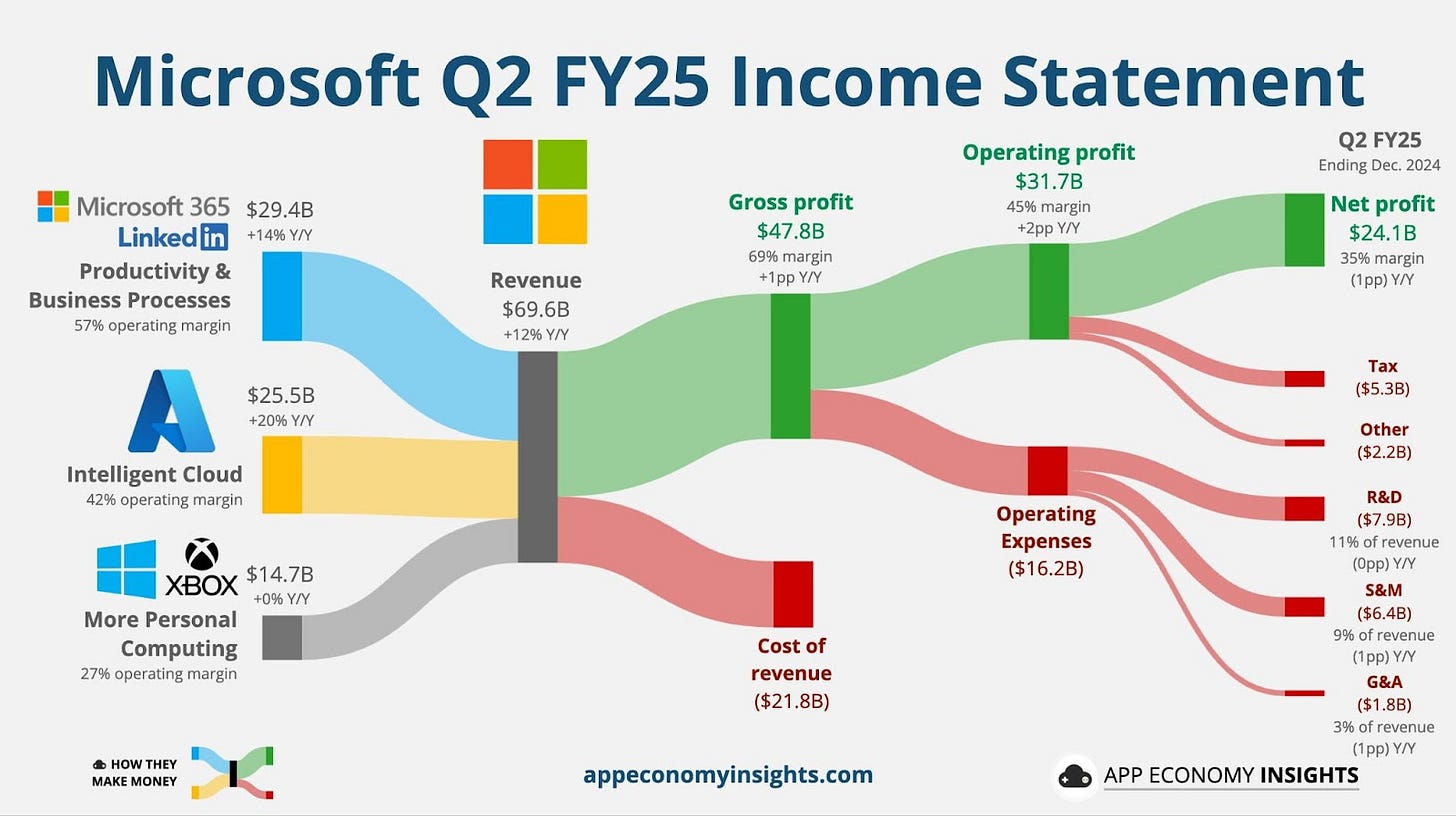
Microsoft’s earnings and AI strategy
There are three main conclusions after last yesterday's quarter call:
1/ Microsoft’s AI growth is limited by infrastructure, not demand
Azure’s 31% growth, though solid, fell at the lower end of expectations, primarily due to data center constraints rather than a lack of AI demand. Microsoft is pouring $80 billion into AI infrastructure this fiscal year, but capacity bottlenecks remain a short-term challenge. The company expects relief by mid-year, reinforcing the idea that AI demand is far outpacing the industry’s ability to supply it.
2/ Microsoft is quietly pivoting its AI strategy
Initially, Microsoft framed its AI investments as a durable cost advantage, leveraging exclusive infrastructure for OpenAI’s models. But now, the tone has shifted because the models are becoming commoditized, and Microsoft is focusing on “database fungibility” and inference cost reduction. This suggests Microsoft no longer sees AI infrastructure as a moat but rather as a flexible, constantly evolving asset.
3/ OpenAI relationship is evolving, but Microsoft maintains leverage
The Stargate announcement and OpenAI’s ability to work with other cloud providers suggest a loosening of Microsoft’s exclusive grip. However, Microsoft still retains right-of-first-refusal on OpenAI’s AI buildout, ensuring it can absorb excess capacity and remain OpenAI’s key infrastructure partner. This dynamic hints at a future where OpenAI operates more independently, but Microsoft continues to benefit from its growth. WSJ, Microsoft
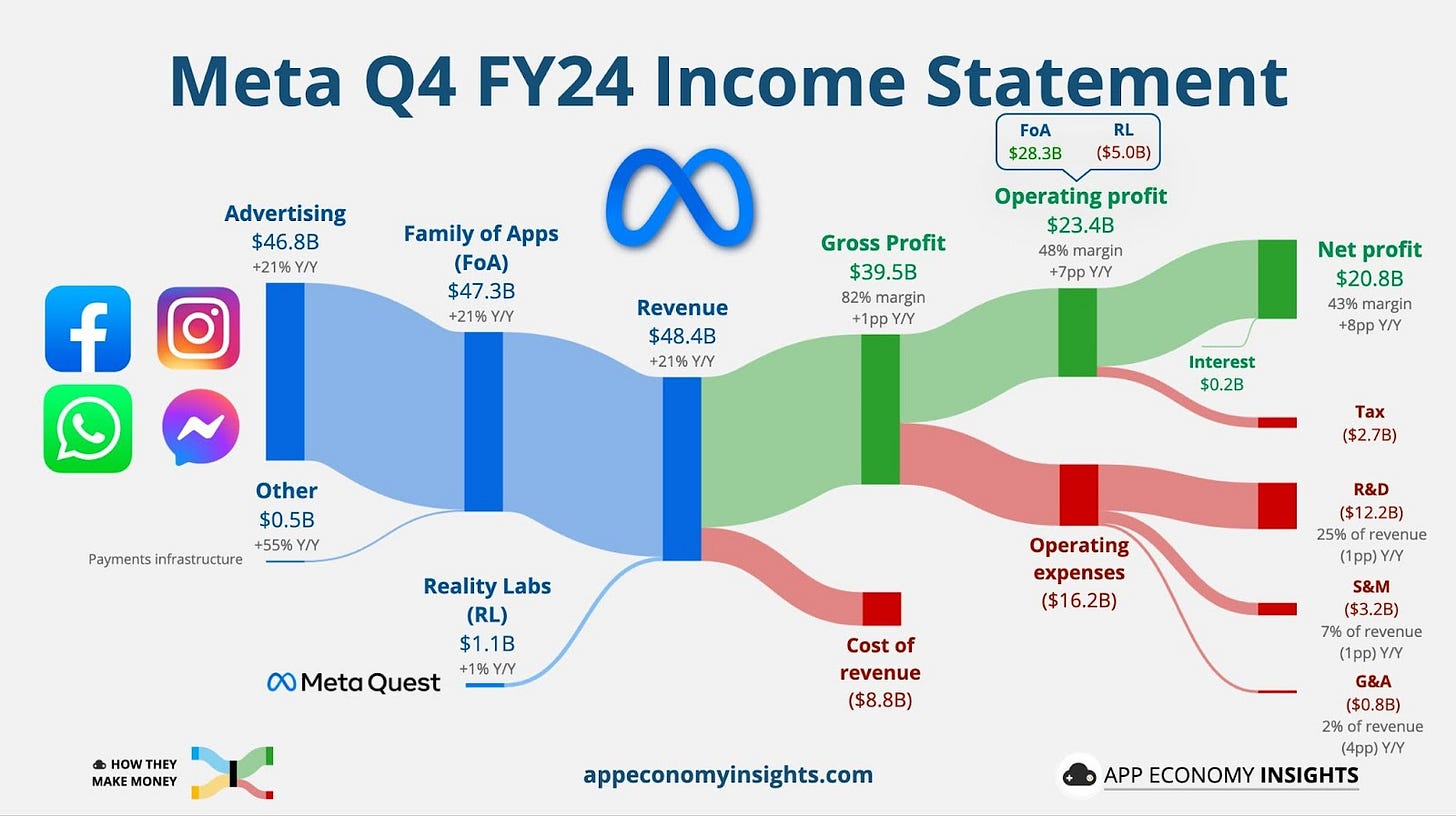
The bull case for META
Three insights from yesterday’s quarterly earnings:
1/ Meta’s AI-driven ad business is its secret weapon
While other tech giants struggle with AI monetization, Meta is already reaping the benefits. Its Andromeda AI system has significantly improved ad targeting, driving an 8% increase in ad quality and boosting revenue efficiency. Unlike Microsoft or Google, which rely on AI infrastructure spending to create long-term value, Meta has an immediate monetization pipeline, turning AI into a revenue engine today.
2/ Meta’s AI spending is aggressive but justified
With capital expenditures expected to rise 70% over 2024, Meta is betting big on AI infrastructure, including a massive Louisiana data center and a 1.3 million GPU fleet by year-end. While some investors fear runaway costs, the company’s record $20.8 billion net income and widening margins suggest its AI investments are financially sustainable. Unlike Google, which faces AI cannibalizing search revenue, Meta’s AI strategy complements its core advertising model.
3/ Meta’s political and competitive moves are strategic
Beyond AI, Meta is positioning itself politically and competitively for an advantage. It eliminated its fact-checking program, relaxed speech restrictions, and aligned with the Trump administration, likely to avoid future regulatory scrutiny. Meanwhile, with TikTok facing potential bans, Meta stands to capture ad dollars and user engagement, especially through Instagram and Threads. The company is playing a long game, balancing AI, policy, and market positioning to reinforce its dominance. WSJ, META
PRINCIPLES
Working on a start-up
Having worked in large companies before, I know the allure of scale, stability, and structure. But at some point, you need to feel the pulse of a small group—whether it’s a startup or a scrappy, mission-driven team. There’s an energy in small groups that’s impossible to replicate in big organizations. It’s raw, it’s intense, and it’s deeply personal.
In a small group, you’re not just a cog in a machine; you’re a driver. Every decision, every late night, every win feels magnified because it’s yours. You learn faster, fail harder, and celebrate victories with the people who built it alongside you. It’s not about the size of the organization, it’s about the size of the ownership you feel.
That kind of energy changes you. It reminds you what it’s like to be fully alive at work. Whether you start something of your own or join a tight-knit team, it’s an experience you owe yourself at least once in your career. You might never want to go back. LINK
Where you live shapes who you become
Proximity to the action isn’t just about convenience, it’s about exposure, opportunity, and serendipity. Agglomeration effects are real. Ideas collide, energy amplifies, and momentum builds when you’re in the midst of it.
You can try to recreate the magic from a distance, but it’s never the same. Being where the action is means you’re part of the conversation before it becomes a headline. You see trends forming, relationships building, and opportunities emerging in real-time.
If you’re serious about growth – personal, professional, or creative – put yourself in the places where people are pushing boundaries and making things happen.
It’s not just about what you’ll do there; it’s about who you’ll become by being part of it. LINK
I just launched my book on strategy:
Through 28 chapters I covered three parts: (1) Strategy, (2) Innovation & Growth, and (3) Generative AI.
See a full sample - the chapter on Network Effects. - click HERE
But the E-Book: https://book.onstrategy.eu
Buy a hardcopy on EMAG
Buy it for Kindle on Amazon